Welcome to the autoimmune diseases website | |||
| CONTACT through services link See Home page for updated info. | |||
| A guide to reverse and prevent all diseasese-book
Celiac Disease & neurological Variants Neurological manifestations of gastric disorders, particular reference to multiple sclerosis.Dr. Zaffaroni M.Universitą di Milano, Gallarate, Varese, Italy. Neurological manifestations of gastrointestinal disorders , with particular reference to those resembling multiple sclerosis (MS) on clinical or MRI grounds. Patients with celiac disease can present cerebellar ataxia, progressive myoclonic ataxia,myelopathy, or cerebral, brainstem and peripheral nerve involvement. Antigliadin antibodies can be found in subjects with neurological dysfunction of unknown cause, particularly in sporadic cerebellar ataxia ("gluten ataxia"). Patients withWhipple's disease can develop mental and psychiatric changes, supranuclear gaze palsy (cannot look up), upper motoneuron signs (weakness stiffness), hypothalamic dysfunction (sleep & sex issues), cranial nerve abnormalities, seizures (epilepsy), ataxia (difficulty walking or walking like a drunk) , myorhythmia (rhythmic alternating movement of any part of body) and sensory deficits like numbness, burning sensations. Neurological manifestations can complicate inflammatory bowel disease (e.g. ulcerative colitis andCrohn's disease) due to vascular or vasculitic mechanisms. Cases with both Crohn's disease and MS or cerebral vasculitis are seen in many people. Epilepsy, chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy, muscle involvement and myasthenia gravis are also reported. The central nervous system can be affected in patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection because of vasculitis associated with HCV-related cryoglobulinemia. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy (MNGIE) is a disease caused by multiple deletions of mitochondrial DNA. It is characterized by peripheral neuropathy, ophthalmoplegia, deafness, leukoencephalopathy, and gastrointestinal symptoms due to visceral neuropathy. So its very important to consider Celiac disease as causing any disease from Alzheimer's to CIDP, MS or epilepsy.
Neurol Sci. 2001 Nov;22 Suppl 2:S117-22.-------------------------------------------------------- Neurological manifestations can be the consequence of vitamin B1, nicotinamide, vitamin B12, vitamin D, or vitamin E deficiency and from nutritional deficiency states following gastric surgery. Federal University of Cearį, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil. Celiac disease (CD/ Nontropicalsprue, gluten-sensitive enteropathy) is a malabsortive condition in which an allergic reaction to the cereal grain-protein gluten (present in wheat, rye and barley) causes small intestine mucosal injury. The onset is in the first four decades of life, with a female to male ratio of 2:1. It may be associated with a wide spectrum of neurological manifestations including cerebellar ataxia, epileptic seizures, dementia, neuropathy, myopathy and multifocal leucoencephalopathy. We report three patients with neurological manifestations related with CD: one with cerebellar ataxia, one with epilepsy and one with cognitive impairment. The diagnosis of CD was confirmed by serologic tests (antiendomysial and antigliadin antibodies) and biopsy of the small intestine. In two patients the neurological symptoms preceded the gastrointestinal abnormalities and in all of them gluten restriction failed to improve the neurological disability. CONCLUSION: CD should be ruled out in the differential diagnosis of neurological dysfunction of unknown cause, including ataxia, epilepsy and dementia. A gluten free diet, the mainstay of treatment, failed to improve the neurological disability. However CIDPUSA does provide alternatives to help CELIAC read our e-book to help reverse the disease naturally. Please continue to next page and read Neuropathy in celiac disease |
| ||
| www.cidpusa.org/P/ivig.htm Study showing ALS is Cidp ALS story MMF & ALS | |||
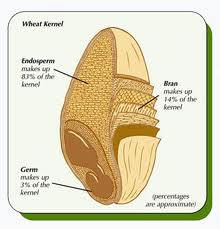 No Wheat
No Wheat 