Nerve physiology
Axonal Polyneuropathy changes in EMGEMG/NCV section Learn about the Brain Learn about nerves Nerve Fibers conduction described in detail below.
SynapsesContinued from Saltatory conduction
Neuroglial, or glial, cells - general functions include:
- 1 - forming myelin sheaths
2 - protecting neurons (via phagocytosis)
3 - regulating the internal environment of neurons
in the central nervous system
Synapse = point of impulse transmission between neurons; impulses are transmitted from pre-synaptic neurons to post-synaptic neurons
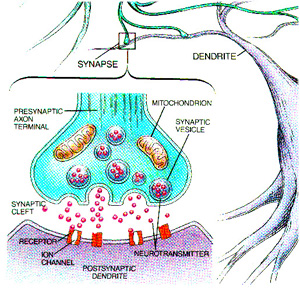
Synapses usually occur between the axon of a pre-synaptic neuron & a dendrite or cell body of a post-synaptic neuron. At a synapse, the end of the axon is 'swollen' and referred to as an end bulb or synaptic knob. Within the end bulb are found lots of synaptic vesicles (which containneurotransmitter chemicals) and mitochondria (which provide ATP to make more neurotransmitter). Between the end bulb and the dendrite (or cell body) of the post-synaptic neuron, there is a gap commonly referred to as the synaptic cleft. So, pre- and post-synaptic membranes do not actually come in contact. That means that the impulse cannot be transmitted directly. Rather, the impulse is transmitted by the release of chemicals called chemical transmitters (or neurotransmitters).


Synapses between axon of pre-synaptic neuron & dendrite illustarted
Continued to how the nerve cell works or neuron physiology
-
- CIDP DIAGNOSIS
- Treatment CIDP
- M.M.F.
- Metal toxicity and learning
- Vitamin-C
- A normal EMG/NCV in CIDP
- Lymes
- Axonal EMG
- Painful neuropathy
- Muscle Histology
- Nerve types
Autoimmune cause
Key words : action, potential, nerve, membrane, depolarizes, negative, electron;